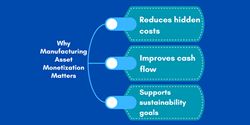
Manufacturing Asset Monetization: What It Is and How It's Done
This article will explain what manufacturing asset monetization is, outline the main methods companies use, and walk through the process step by step.
How Freight Visibility Is Redefining U.S. Manufacturing Supply Chains
With freight visibility, you can search for alternative sources and routes when shipments hit a snag. You can find the best ways to increase your resources for demand spikes, and you can search for the most cost-effective solutions during demand droughts.
The 'Halo Effect' of Manufacturing Facility Location: Why Smart Manufacturers Are Choosing Locations Near Complementary Businesses
This strategy is not about simple convenience; it's about creating a powerful, mutually reinforcing "halo effect" of shared success, instant market credibility, and profound operational synergy across engineering, tooling, fabrication, and logistics networks.
Manufacturing's AI Reality Check: Why Governance Is the Missing Link
Governance is the architecture that transforms AI experiments into enterprise assets. Without it, even successful models become liabilities.
Strengthening Cybersecurity Measures as Threat Actors Set Their Sights on the Manufacturing Industry
To manage these risks at scale, organizations need modern Privileged Access Management (PAM). Unlike legacy access controls, modern PAM enforces least-privilege access, monitors high-risk accounts in real time and integrates seamlessly with broader security ecosystems.
How Real-Time Manufacturing Operations Drive Competitive Advantage in Volatile Markets
Manufacturing executives confronting today's operational challenges recognize a fundamental truth: traditional execution systems designed for stable markets have become organizational liabilities.
How to Employ AI in Manufacturing Sales
AI agents can help ensure every interaction across every channel contributes to a single, intelligent sales motion, including always-on gathering insights like on which SKUs are trending to develop and implement real-time optimizations.
"Building for the Surge: How to Prepare Your Factory Storage for Times of Peak Demand"
To truly manage seasonal peaks efficiently and safely, facilities need a storage infrastructure designed to flex with changes in demand, regardless of whether they're seasonal, planned, or one-time occurrences.
The Data Imperative for Smart Microfactories: Enabling Real-Time Agility and Resilience
Microfactories, digital twins, and AI-first manufacturing strategies are not science fiction, they are here. But their success depends not just on sensors and robotics, but on how well data is connected, contextualized, and consumed.
Understanding End-to-End Configuration: A Primer
End-to-end configuration offers a strategic solution for unifying data, improving collaboration across departments, and enabling scalable, service-ready product operations.
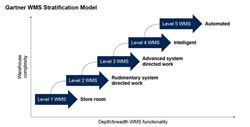
How Gartners 10 Dimensions of Warehouse Complexity can Transform your WMS Strategy
A strong WMS should balance simplicity and depth, offering configurability without extensive custom code, seamless integration with material handling systems, and robust tools for labor management, task orchestration, and automation.
Top 5 AI-Powered Capabilities to Look for in a WMS Vendor
Success depends on how deeply and thoughtfully those capabilities are embedded into the system. As you evaluate vendors, look beyond the buzzwords and focus on practical AI tools that deliver faster deployment, smarter execution, and long-term flexibility.
Beyond Automation: How Software is Redefining Industrial Machinery
Software-Defined Machinery (SDM) leads the transformation where the capabilities and performance of industrial assets are determined by sophisticated software. When paired with AI, this software unlocks a new realm of capability, efficiency, and innovation.
4 Robotic Finishing Techniques for High-Precision Manufacturing Applications
Manufacturing leaders interested in implementing robotic finishing techniques should carefully plan and focus on seamless integration. They should consider how these advanced technologies fit into their existing facilities and prioritize employee training.
Beyond the Camera: Network Choices that Impact Machine Vision Systems
As automation accelerates, understanding the network that connects hardware with software will help ensure that machine vision systems operate at their full potential.
Records 1 to 15 of 699
Automation & IIoT - Featured Product

Model TR1 Tru-Trac
The Model TR1 Tru-Trac® linear measurement solution is a versatile option for tracking velocity, position, or distance over a wide variety of surfaces. An integrated encoder, measuring wheel, and spring-loaded torsion arm in one, compact unit, the Model TR1 is easy to install. The spring-loaded torsion arm offers adjustable torsion load, allowing the Model TR1 to be mounted in almost any orientation - even upside-down. The threaded shaft on the pivot axis is field reversible, providing mounting access from either side. With operating speeds up to 3000 feet per minute, a wide variety of configuration options - including multiple wheel material options - and a housing made from a durable, conductive composite material that minimizes static buildup, the Model TR1 Tru-Trac® is the ideal solution for countless applications.
Manufacturing and Automation - Featured Company

FAULHABER MICROMO
Since 1961, FAULHABER MICROMO has partnered with OEMs to deliver high precision, high performance, custom micro motion system solutions to markets such as medical, robotics and automation in North America. FAULHABER MICROMO's tradition of innovation started decades ago in Germany. The groundbreaking invention of the FAULHABER coreless winding started it all for a market that produces millions of motors today.
How can the FAULHABER MICROMO team help you deliver your next innovation to market first?
Learn more about MICROMO's solutions for the most demanding applications, our diverse motion products and technologies, online ordering, Engineering and R&D teams, Clean Room Assembly, Machining Center and other services at our Clearwater, FL facility at www.micromo.com.

.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)



.jpg)

