UMN researchers create new 3D printing method
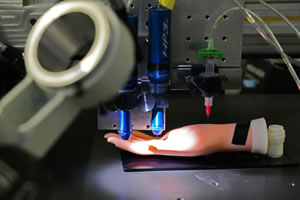 Sydney Baum-Haines for Minnesota Daily: A team of University of Minnesota scientists has developed a futuristic method of 3D printing.
Sydney Baum-Haines for Minnesota Daily: A team of University of Minnesota scientists has developed a futuristic method of 3D printing.
Michael McAlpine, associate professor of mechanical engineering at the University, and his lab created a new method of 3D printing that prints working electronics on uneven surfaces. His team believes this research could be the first step towards printing on human skin.
The research was published online in May in the academic journal “Advanced Materials.”
“We’re trying to expand the capabilities of 3D printing from hard plastic to what we call functional materials,” McAlpine said.
Printing electronic materials has a variety of possible applications, many of which are medical, he said. McAlpine foresees that surgical robots could be enhanced to send surgeons controlling them signals of what they feel using this method. Other uses could include printing sensors onto prosthetic limbs to give the wearers feeling. Full Article:
Featured Product

